Page 240 - University of South Florida Student Planner 2022-2023
P. 240
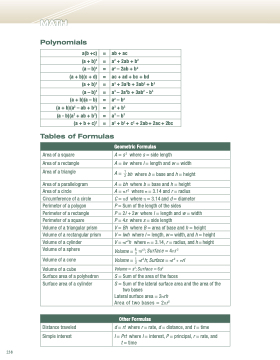
MATH Polynomials
a(b +c)
=
ab + ac
(a + b)2
=
a2 + 2ab + b2
(a – b)2
=
a2 – 2ab + b2
(a + b)(c + d)
=
ac + ad + bc + bd
(a + b)3
=
a3 + 3a2b + 3ab2 + b3
(a – b)3
=
a3 – 3a2b + 3ab2 - b3
(a + b)(a – b)
=
a2 – b2
(a + b)(a2 – ab + b2)
=
a3 + b3
(a - b)(a2 + ab + b2)
=
a3 – b3
(a + b + c)2
=
a2 + b2 + c2 + 2ab + 2ac + 2bc
Tables of Formulas
Geometric Formulas
Area of a square
A = s2 where s = side length
Area of a rectangle
A = lw where l = length and w = width
Area of a triangle
A = 12 bh where b = base and h = height
Area of a parallelogram
A = bh where b = base and h = height
Area of a circle
A = π r 2 where π = 3.14 and r = radius
Circumference of a circle
C = πd where π = 3.14 and d = diameter
Perimeter of a polygon
P = Sum of the length of the sides
Perimeter of a rectangle
P = 2l + 2w where l = length and w = width
Perimeter of a square
P = 4s where s = side length
Volume of a triangular prism
V = Bh where B = area of base and h = height
Volume of a rectangular prism
V=lwh wherel=length,w=width,andh=height
Volume of a cylinder
V = πr 2h where π = 3.14, r = radius, and h = height
Volume of a sphere
Volume = 43 πr 3; Surface = 4πr 2
Volume of a cone
Volume = 13 πr2h; Surface = πr2 + πrl
Volume of a cube
Volume = s3; Surface = 6s2
Surface area of a polyhedron
S = Sum of the area of the faces
Surface area of a cylinder
S = Sum of the lateral surface area and the area of the two bases
Lateral surface area = 2πrh Area of two bases = 2πr2
Other Formulas
Distance traveled
d = rt where r = rate, d = distance, and t = time
Simple interest
I = Prt where I = interest, P = principal, r = rate, and t = time
238